The Technical Principle Of LED Street Lights
Traditional LED street lamp design mainly focuses on the number of lumens of the LED, while less attention is paid to heat dissipation. In fact, the lumens of LEDs are increasing rapidly. The number of lumens per watt of mass-produced LEDs in 2019 has reached 160 lumens, and this value is still growing rapidly. The corresponding theoretical system of heat transfer has matured, and the heat transfer methods we can use are basically clear: conduction, convection, radiation and phase change heat transfer. Therefore, in terms of heat transfer or heat dissipation, the measures we can take are visible and limited.
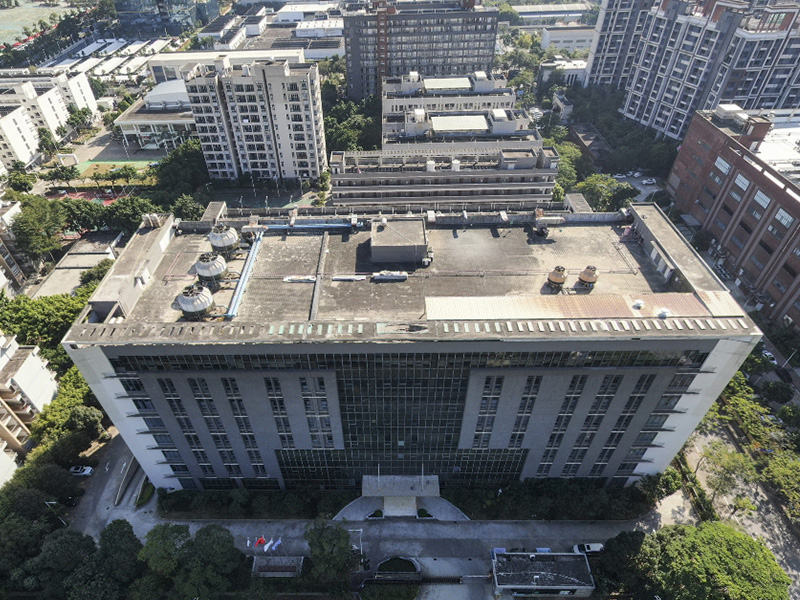
The heat dissipation technology of LED street lamps generally uses a heat-conducting plate, which is a 5mm thick copper plate, which is actually a temperature equalizing plate, which equalizes the temperature of the heat source. There are also heat sinks to dissipate heat, but the weight is too large. Weight is very important in the street lamp system, because the street lamp is 9 meters high, if it is too heavy, it will increase the risk, especially in the event of typhoons and earthquakes. Accidents may occur. Domestic manufacturers use the world’s first needle-shaped heat dissipation technology, needle-shaped radiator The heat dissipation efficiency of the radiator is greatly improved compared with the traditional fin radiator, which can make the junction temperature of the LED more than 15℃ lower than that of the ordinary radiator, and the waterproof performance is better than that of the ordinary aluminum radiator. At the same time, the weight and volume are also improved. In addition, the graphite heat sink developed for high-power LED lamps also has good heat conduction and heat dissipation performance.
The main heat dissipation methods are: natural convection heat dissipation, forced heat dissipation by adding fans, heat pipe and loop heat pipe heat dissipation, etc. The forced heat dissipation method of installing a fan has a complicated system and low reliability, and the heat dissipation method of heat pipe and loop heat pipe is costly. The street lamp has the advantages of outdoor night use, the heat dissipation surface is located on the side, and the body shape is less restricted. It is beneficial to the natural convection and heat dissipation of the air. Therefore, it is recommended to choose the natural convection heat dissipation method as much as possible.
The problems in the heat dissipation design of LED street lights are: the area of the heat dissipation fins is set at will, the arrangement of the heat dissipation fins is unreasonable, and the arrangement of the heat dissipation fins of the lamps does not take into account the use of the lamps, which affects the effect of the fins, and emphasizes heat conduction. Ignore convection and heat dissipation. Although many manufacturers consider various measures: heat pipes, loop heat pipes, adding thermal grease, etc., they do not realize that the heat will eventually be dissipated by the outer surface of the lamp. Ignore The balance of heat transfer, if the temperature distribution of the fins is severely uneven, it will cause some of the fins to have no effect or have a limited effect.
Heat-dissipating high-power LED street light fixtures. Its purpose is to solve the heat dissipation problem of high-power LED lamps and propose a high-power LED street lamp lamp with air convection heat dissipation, which includes a lamp head assembly, a lamp heat sink assembly and a lamp tail assembly. The lamp heat sink assembly is an arc-chord cylindrical shell, Open at both ends, both sides of the arc cylindrical surface are vertical surfaces, and the vertical surface is also provided with array of through holes. In the inner cavity of the arc-chord cylindrical shell, there are 4-10 axially arranged and aligned with the arc cylindrical surface and the chord cylindrical surface. The two vertical sides of the vertical rib heat conduction plate and the vertical rib heat conduction plate and the arc-chord cylindrical shell are also provided with array through holes. The vertical rib heat conduction plate and the two vertical ribs on both sides of the arc-chord cylindrical shell 5-11 heat dissipation channels for hot air flow are formed in the radiator assembly of the lamp. The utility model has the advantages that there are multiple heat dissipation channels through which hot air flows in the cavity of the heat dissipation body, and the vertical rib heat conduction plate also serves as a heat dissipation surface, the heat exchange surface is increased, and the heat discharge efficiency is high.
The heat dissipation of LED street lamps is one of the key problems that need to be solved. Not only is it directly related to the luminous efficiency of the LED in actual work, but also because the LED street lamp has high brightness requirements and large heat generation, and the outdoor environment is relatively harsh, if the heat dissipation is not good It will directly lead to rapid aging of the LED and lower stability. Because road lamps used outdoors should have a certain level of dust and water resistance (IP), good IP protection often hinders the heat dissipation of LEDs. Solving these two contradictory problems that both have to be solved is an important aspect that should be paid attention to when designing road lamps. In this respect, it is also the most unqualified and unreasonable situation when LED is applied to road lamps in China. The unqualified and unreasonable situations in domestic use basically include:
(1) A radiator is used for the LED, but the design of the terminal and the radiator of the LED connection cannot reach IP45 and above, and cannot meet the requirements of the GB7000.5/IEC6598-2-3 standard.
(2) Using ordinary road lamp housing, matrix LED is used in the light emitting surface of the lamp. Although this design can meet the IP test, the temperature of the inner cavity of the lamp will increase due to the lack of ventilation in the lamp. At 50°C~80°C, under such high working conditions, the luminous efficiency of the LED is unlikely to be high, and the service life of the LED will also be greatly reduced. In fact, there is an obvious unreasonable situation.
(3) The instrument fan is used in the luminaire to dissipate the LED and radiator. The air inlet is designed under the luminaire to prevent rainwater from entering, and the air outlet is designed around the downward LED light source. This can also effectively prevent rainwater from entering. In addition, the radiator and the LED (light source cavity) are not in the same cavity. If this design is done well, it can pass smoothly according to the IP test requirements of the lamp. This solution not only solves the heat dissipation problem of the LED, but also meets the requirements of the IP level. But this seemingly good design is actually obviously unreasonable. Because in most road lighting applications in our country, the amount of fly dust in the air is relatively large, sometimes reaching a large amount (such as sandstorms). This type of lighting is used for a period of time under normal conditions (about three months to Half a year), the gap of the internal radiator will be filled with dust, which will greatly reduce the effect of the radiator. Finally, the service life of the LED will be significantly shortened due to the excessively high operating temperature. The disadvantage of this scheme is that it cannot be used consistently and well.
To take into account the heat dissipation and IP protection of LEDs in road lamps, a more reasonable design guideline is:
a. Use a thermal conductive plate at the critical heat dissipation position. The heat-conducting plate is inside the metal plate. Thin pipes for the flow of refrigerant are evenly distributed. The thin pipes are filled with refrigerant. When a certain part of the heat-conducting plate is heated, the refrigerant in the thin pipes will flow quickly and the heat will be rapid. Ground conduction. The thermal conductivity of a good thermal conductive plate can reach 8-12 times that of a copper plate with the same thickness. Although the price is higher, if it is used in key parts, it will play a double role in the heat dissipation of the LED.
b. Design the shell of the lamp into a radiator shape. Most road lamp housings are made of aluminum. Using the outside of the lamp housing directly as a radiator can not only ensure the requirements of IP protection level, but also obtain a large heat dissipation area. In addition, when the radiator composed of the lamp housing is dusty, It can be washed through natural wind and rain, so as to ensure the continuous effectiveness of the radiator.